How Much Cobalt Is in the World?
Cobalt is a hard silver-gray metal primarily used in batteries, particularly lithium-ion batteries utilized to power anything from cell phones and laptops to electric vehicles. Additionally, cobalt has applications in alloys (mainly high-strength alloys used in the aeronautical, energy, and defense sectors), catalysts, magnets, and cutting tools.
As of 2022, the global reserves of cobalt amount to 8.3 million metric tons. Cobalt is not particularly rare (ranking 32nd in the global abundance of metals), however, due to its many applications and the expanding EV sector, demand for this mineral should continue to increase. In fact, it is estimated that global demand for cobalt use in batteries will reach 117,000 tons by 2025.
Read on for more information on the cobalt industry, including the biggest producers, key players, and the toll cobalt mining has taken on people and the environment.
Key Facts and Statistics to Remember
- The Democratic Republic of Congo accounts for over 70% of total cobalt production.
- The cobalt market was worth around $8.4 billion in 2021.
- China is the biggest refined cobalt producer, accounting for 76% of global production.
- Secondary supply from recycling accounts for 5% of production.
- China accounts for 32% of global demand.
- Demand for cobalt witnessed an annual increase of 13% in 2022.
- Nearly 2,000 people die a year in artisanal mines in the DRC.
Which Country Is the Largest Producer of Cobalt
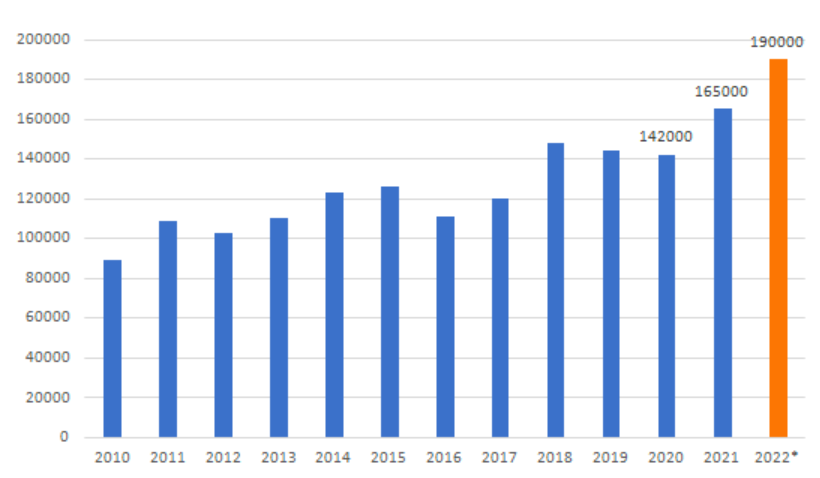
1. 190,000 metric tons of cobalt were produced in 2022.
Representing an increase from the 165,000 metric tons produced in 2021 and 142,000 MT in 2020, 2022’s total worldwide production peaked at 190,000 MT.
2. The Democratic Republic of Congo accounts for over 70% of total cobalt production.
The Democratic Republic of Congo is by far the biggest producer of cobalt across the globe — in 2022, it produced 130,000 metric tons of cobalt, taking up more than 70% of global cobalt production.
DRC is followed by:
- Indonesia: 10,000 MT
- Russia: 8,900 MT
- Australia: 5,900 MT
- Canada: 39,000 MT
- Cuba: 3,800 MT
- Philippines: 3,800 MT
- Papua New Guinea: 3,000 MT
- Madagascar: 3,000 MT
- Turkey: 2,700 MT
- Other countries: 5,200 MT
The US has a production volume of 800 metric tons, the lowest of the cobalt-producing countries worldwide. Even though the country exports some cobalt, it mostly relies on imports and secondary (scrap) materials to meet its cobalt needs.
It’s worth noting that Indonesia became the second-largest producer of cobalt in 2022. The country is slowly emerging as a big player in the cobalt market — experts estimate that Indonesia has the potential to increase cobalt supply by 10 times over the next 7 years.
3. Where is cobalt found in the world?
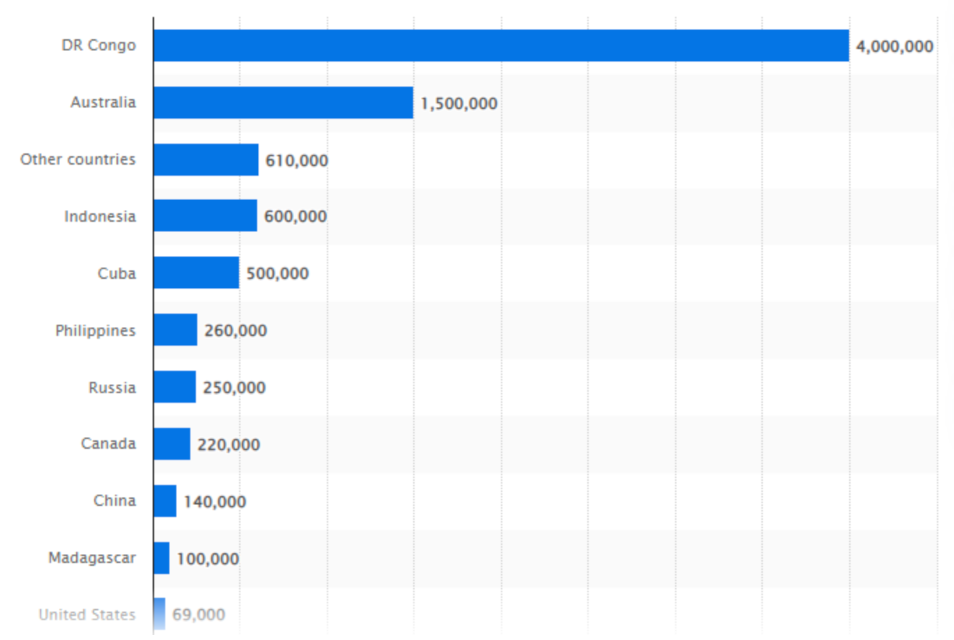
Estimated at 4 million metric tons, the Democratic Republic of the Congo has the largest cobalt reserves in the world.
Australia is in second place holding 1.5 million metric tons in cobalt reserves, followed by Indonesia and Cuba with 600,000 and 500,000 MT of cobalt, respectively.
4. With an output of 55,908 metric tons, the Metalkol RTR Project in DR Congo is the largest cobalt-producing mine in the world.
The top cobalt mines in terms of production are located in the DRC, however, seven out of ten are Chinese-owned.
The biggest one, the Metalkol RTR Project, is owned by Eurasian Resources Group Sarl and is located in Katanga. In 2021, it reported an output of 55,908 tons and around 4.78 million MT per annum in run-of-mine ore.
The second largest was the Tenke Fungurume Mine. Owned by China Molybdenum Co, this mine had a production volume of 18,501 metric tons in 2021. The third biggest is the Mashamba East Mine (17,775 tons), followed by the Sicomines Copper-Cobalt Mine (17,154 tons) and the KOV Mine (16,491 tons).
The five biggest cobalt mines in the world produced a combined total of 125,829 MT in 2021.
5. Roughly 12% of cobalt production comes from small-scale, artisanal mines in the DRC.
About 14.5 kt of cobalt mined in the DRC comes from small-scale mines where independent miners use their own resources to extract the mineral.
It is estimated that artisanal mining employs between 150,000 and 200,000 people in the DRC, while a million more are indirectly involved in the industry trade and transport. Adults and children involved in artisanal cobalt mining often work in dangerous environments without the proper protection which has led to several life-threatening accidents, as well as long-term respiratory and skin issues.
How Big Is the Cobalt Mining Industry
6. The cobalt market was worth around $8.4 billion in 2021.
According to the latest reports, the cobalt market increased by 90% since 2020 when it was valued at approximately $4.4 billion.
The market value of cobalt is expected to go up from around $8.4 billion in 2021 to $17.39 billion in 2027. The market volume, on the other hand, is anticipated to increase from 99,300 MT recorded in 2017 to almost 200,000 MT by 2025 — showing growth of more than 100%.
7. The global cobalt industry provided 863,000 jobs in 2021.
This represents a threefold increase since 2010 when the industry provided just 288,000 jobs. Estimates show that the number of jobs in the sector will increase to 1.5 million by 2030.
Three out of four jobs in the cobalt industry are indirect, i.e. related to subcontracting services, refining, and battery production.
8. Total worldwide refinery production of cobalt stood at 144 kt in 2022.
Refining is required for most applications, including EV batteries. In 2022, primary refined production increased by 14% year-on-year. China is still the biggest refined cobalt producer, accounting for 76% of global production. The country also refined 91% of the world’s cobalt chemical supply in 2022.
9. With a total production of 25,320 MT, Glencore is the biggest cobalt-producing mining company.
Glencore supplies some of the biggest battery manufacturers in the world, including Tesla (purchasing 6,000 tons a year of the battery cathode material), Samsung SDI (21,000 tons), SK Innovation (30,000 tons), and GEM Co. (61,200 tons).
The Swiss multinational company is followed by the Eurasian Resources Group (total production of 20,700 MT) and China Molybdenum (14,800 MT), which is partly owned by the Chinese government.
Gecamines (13,860 MT), a Congolese state-controlled mining company, and China-based Zhejiang Huayou Cobalt (5,390 MT) round off the top five players in the cobalt mining industry.
How Long Will Cobalt Reserves Last
10. How much cobalt is left in the world?
There are 8.3 metric million metric tons of cobalt reserves left in the world.
Cobalt is ranked 32nd in global abundance among metals, which means that it is not particularly rare. However, due to increased demand, mainly fueled by the rise in EV sales (forecast to go up 62 million units per year by 2050), demand is expected to outpace supply in the long term.
In terms of resources, as of 2021, identified world terrestrial cobalt resources are about 25 million tons, while global ocean resources are estimated at 120 million tons.
11. Is there enough cobalt to meet the need for batteries?
According to the Cobalt Institute, supply will outpace demand in the short term. However, in the long term, supply is forecast to grow at a slower pace than demand, i.e. 6% vs. 10% CAGR, respectively, which means the market will face a structural deficit, presumably between 2028 and 2033.
However, the needs of the EV sector can still be met provided recycling takes up a larger share of production. Currently, secondary supply from recycling accounts for just 5% of the 122 kt produced in 2022. That said, it is predicted that the share of secondary supply of cobalt will increase to 15% by 2030 and up to 52% by 2050 as recycling capabilities increase and more battery scrap is made available.
Cobalt Consumption by County
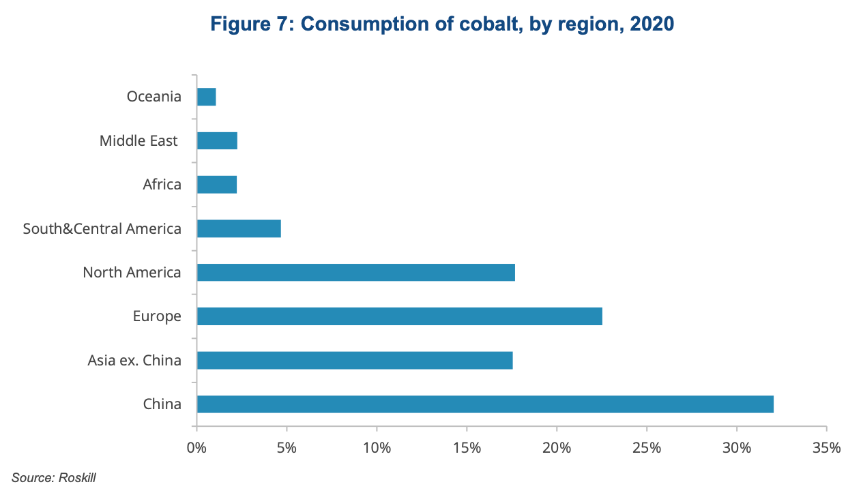
12. Asia consumes about 50% of worldwide cobalt production.
In terms of regions, Asia is the biggest consumer of cobalt with China, where 80% of cobalt consumption is used by the rechargeable battery industry, taking the lead and accounting for 32% of global demand (an estimated 44kt). The rest of Asia takes up almost 17.6% of global consumption.
North America and Europe also consume large amounts of cobalt, taking up a combined share of 40% of worldwide consumption. In these regions, the main application of cobalt is in batteries, tool materials, and nickel-based alloys.
13. Demand for cobalt witnessed an annual increase of 13% in 2022.
Although this is a weaker growth compared to the 27% year-on-year increase in 2021, demand for cobalt was on the rise across the globe. In 2022, total worldwide demand increased to 187 kt from 21 kt the previous year. Consumption is expected to rise by 108% by 2030, reaching nearly 388 kt and growing at a CAGR of 10%.
14. Accounting for 40% of the total market, the EV sector is the largest end-user of cobalt.
Since 2021, the EV sector has been the biggest end-user of cobalt, contributing 86% of total growth in cobalt demand. In fact, demand from this sector reached 74 kt in 2022 and it is expected to grow further thanks to the growing popularity of electric vehicles and government incentives geared towards clean energy use.
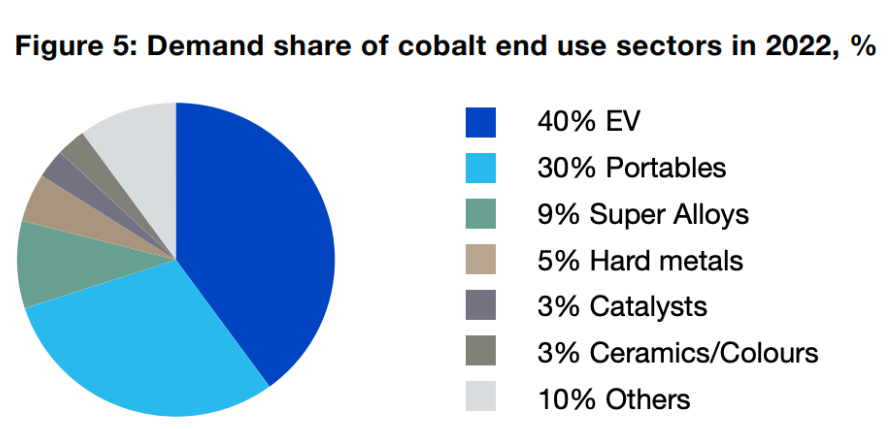
15. Batteries account for 72% of cobalt demand.
The most common use of cobalt is its application in lithium-ion and other batteries. In fact, non-battery applications accounted for a 28% share of demand in 2022 and contributed just 6% of growth to the industry.
In the US, 40% of cobalt consumed is used in superalloys (primarily in aircraft gas turbine engines), 35% is used in chemical applications and 15% in other metallic applications.
Human Cost of Cobalt Mining
16. Around 40,000 of the workers in artisanal mines in the DRC are children.
Some of these children are as young as six years and get paid less than $2 a day for the work they do, most of which is carried out by hand without any protective gear or masks. Children are believed to work 12 hours a day in the mines either in deep underground shafts around 10 meters long or on the surface collecting, sorting, and washing this radioactive mineral.
17. Nearly 2,000 people die a year in artisanal mines in the DRC.
Although based on cases reported in the media, the World Bank puts the number of fatalities at 65, the actual figure is much higher reaching about 1% of the workforce. In fact, the median age for artisanal cobalt miners in the DRC is 25 years.
18. Southern Katanga, home to the biggest cobalt mines, is one of the 10 most polluted areas in the world.
Millions of trees have been cut by mining companies in the Congo Basin, the second-biggest rainforest.
In addition to deforestation, cobalt mining has been linked to water pollution and crop contamination. Cobalt is also classified as a ‘possible’ carcinogen, which means high concentrations of the mineral in fish and drinking water pose a threat to human health as well. Cobalt mining also generates high emissions of carbon dioxide and nitrogen dioxide adding to Africa’s contribution of 5% of carbon dioxide emissions globally.
What’s more, recent research has shown that the likelihood of birth defects increases significantly when parents have worked in a copper or cobalt mine with people in the African “copperbelt” (the mining area in the DRC and Zambia) being particularly at risk.



