Complete guide of Lighting Terms and Metrics
This article will help you to not get confused with all sorts of terms, metrics and abbreviations used to describe various types of lighting fixtures. I have briefly explained most of the terms you will encounter when looking at either wired, portable and solar lights or even light bulbs, so you have all the information needed to purchase the best lighting fixture for your situation. This article will be updated with fresh information in the future. There are “more information” links at the end of most categories where you can find more in-depth information about that category. Hope you find the article useful and let me know if you have any questions or additions with new terms or metrics that you feel should be included in this guide.
Here is a small table of contents with the main categories of terms:
Lighting metrics
Lumens – A lumen is a measurement of light that measures the light output of a lamp to estimate how bright a lamp will be.
Today, lumens are used as the main way to compare different light bulbs and different lamps (although other measurements such as “useful lumens” and “LUX” are also used) to determine which of them is brighter. Generally speaking, the higher the lumen rating of a lamp is, the brighter the lamp is going to be. So if you need a bright outdoor flood light to illuminate your house or backyard, look for a lamp with higher lumen rating, but if you need a dimmer light for your bedroom, get a lamp with less lumens. To measure the number of lumens of a light a special light integrating sphere is used, however, to measure the light output in a given area a device called lux meter is used.
Wattage/watts – Wattage is used to describe an electric power and watt (W) is a unit of power in the International System of Units that measures work done by electricity in a second. Watts can be calculated by multiplying volts (V) with amperes (A). The easiest way to understand watts is by thinking that a 100W light bulb will consumes 100 watt hours of energy in an hour, or in other words, 100W of energy would light a 100W light bulb for one hour.
When CFL and LED bulbs weren’t present, wattage was a common way to measure brightness of a bulb, the higher the wattage, the brighter the bulb is going to be. This is no more true because LED diodes, for example, are much more energy efficient and consume much less wattage to provide the same level of brightness (number of lumens) as old incandescent light bulbs. For example, to produce 800 lumens of light an incandescent bulb will use 60 watts of electricity, CFL bulb about 15 watts and LED bulb less than 10 watts.
Voltage/Volts – Voltage is electric potential difference or difference in charge between two points on a circuit. Voltage is measured in joules per coulombs and the electrical unit of voltage is volt (V).
Volts can also be calculated by multiplying current (amps) with electrical resistance (ohms). An easy way to think of volts, amps, ohms and watts is in this way – volts push amps through ohms that make watts. Regarding lighting, lumens and wattage are much more common terms to describe the power (brightness) of a light bulb, but voltage is mentioned when talking about battery powered solar and portable lighting, as different types of batteries have different voltages.
Ampere, Ampere-hour (Ah), Milliampere-hour (mAh) – An ampere (“amp” in short) is an electrical current measurement unit which is used to measure flow rate of electric charge in an electric conductor at rate of one coulomb per second.
An ampere-hour (Ah) is a unit used to measure amount of electric charge needed for one ampere of electric current to flow for one hour, because 1 ampere equals a flow rate of 1 coulomb of electrons per second, 1 ampere-hour equals 3600 coulombs. So potentially, a battery that has a capacity of 1 Ah could provide 1A current for 1 hour after which it would be fully discharged. As you can guess by now, ampere-hours are used mostly to measure capacity of a battery. To measure capacity of smaller batteries a term milliampere-hour (mAh) is used, 1 mAh = 0,001 Ah which is equal to 3.6 coulombs.
When looking at lighting, you will mostly find ampere-hours and milliampere-hours used to describe capacity of portable and solar flood light batteries. Generally, the greater the number of Ah indicated on the battery, the more charge it can store and provide longer illumination hours for the light when it works on battery.
LUX – Lumens per square meter. LUX is a unit in the SI that is used to measure illuminance or light intensity on a certain area. One lux equals one lumen falling on a one square meter large surface.
In practice, using a bulb that produces 100 lumens which all are concentrated in one square meter large area will measure light intensity of 100 lux at that area, however, using the same bulb to illuminate two square meter large area will produce dimmer 50 lux illuminance. Lux number can be used to measure how many lumens (how bright light) you will need to illuminate a given area, to illuminate a large area you will have to either use brighter light bulbs or multiple lighting fixtures together that will increase the total power consumption of lights. Lux is the most accurate measurement to compare different types of lamps and bulbs when you now which area exactly you want to illuminate. Lux can be measured using a lux meter at the surface being illuminated.
Foot-candle – Lumens per square foot. The meaning of foot-candle is similar to lux, but instead of meters which are SI measurements, it uses traditional American and English units. One foot-candle equals one lumen falling on one square foot large surface, which is approx. 10 lux.
Here is an educational video by Southern California Edison explaining the fundamentals of lumens, lux and foot-candles.
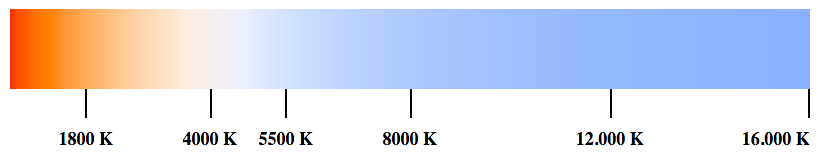
Kelvins (Color temperature) – Color temperature indicates the hue produced by a certain light source and is measured in Kelvins (K).
Color temperature is used to describe color appearance produced by a light source, so basically you can say that color temperature is the color of a light. Each light source has a color temperature that can go from “warmer” red and yellow to “cool” blue, warmer lights have lower color temperature and cooler lights have higher color temperature. The approximate color temperature of different natural and artificial lighting sources is:
- 1700-1900 Kelvins – candle light, flame;
- 2500 Kelvins – incandescent light bulb;
- 3000 Kelvins – halogen light bulb, sunrise and sunset light;
- 4200 Kelvins – CFL, fluorescent light bulbs, early morning light;
- 5500 Kelvins – LED lights (LEDs often come with warmer color temperatures), daylight;
- 7500-10000+ Kelvins – clear, blue sky.
Casing
IP metrics (Waterproof) – IP or Ingress Protection Marking is a common standard that defines level of protection of an electric device against intrusion of foreign objects that can be as large as human hands or as small as dirt and dust and even water.
IP ratings are defined in the following form IP – 65, where first digit (6 in this case) describes the level of solid protection or dust resistance and second digit (5 in this case) describes the liquid protection or water resistance. There are total of 6 solid protection levels and 8 liquid protection levels. You can check out the IP ratings chart with all levels described here.
Actually quite often lighting fixture manufacturers do not indicate the IP rating of a fixture, but instead write that the light is “100% water proof”, “weather proof” and other similar statements. What “waterproof” or “weather proof” actually means is that the lighting fixture is going to have a dust resistance level usually from 4-6 depending whether it is a solar light or a regular wired light (lights with less parts like regular wired flood lights usually have higher IP ratings), and a water resistance level of 4-5 and higher. For most regular and solar flood lights you will see such IP ratings as IP44, IP54, IP55, IP64.
Sealed casing – This indicates that all gaps, mounting holes and other parts of the lighting fixture have been sealed to give the fixture an extra protection against dust and water ingress.
More information about flood light casings
Motion detector
Motion detector/motion sensor – Motion detector is a device that detects motion in a certain operation area. The most common techniques to detect motion is either monitoring an infrared light or transmitting microwaves signals.
Motion sensors are often used together with flood lights, especially solar flood lights. Motion sensing flood lights offer important improvements over regular flood lights such as lower energy consumption and economy, and motion activated lights can be useful in areas where a lighting switch cannot be installed or is not practical to reach. A motion detector is also called a motion sensor.
For flood lights the most common type of sensor used is infrared or PIR sensor. Lighting fixtures that use motion sensor for motion detection are often called “motion activated lights”, “motion sensor lights”, “motion sensing lights”, “PIR lights”, “IR lights”.
Delay time – The amount of time a lighting needs to illuminate when motion is not being detected.
For example, if you set the delay time to 10 minutes, the lighting fixture will be turned off after no motion is being detected in sensors detection range for 10 minutes.
Detection range and distance (Sensitivity) – Detection range indicates how wide angle a motion detector can monitor, this number is expressed in degrees.
For example, most outdoor light motion detectors have a detection range of 180 degrees which means that they can detect motion 180 degrees in the front and on sides of the detector. There are also detectors with smaller and larger detection ranges. For example, some motion sensors can detect motion even 360 degrees around. Lights with such detectors are usually mounted on a pole to provide wide detection range around the lighting fixture.
Detection distance indicates how far from the detector a motion sensor can detect motion and is measured in meters or feet.
Both detection range and distance of a motion sensor are usually called “motion sensor sensitivity” and can be adjusted for most outdoor lights.
PIR/IR/Proximity sensor – A type of motion sensor that detects infrared energy that is emitted from any object that has a temperature above absolute zero.
PIR sensor works by detecting changes of temperature in its monitoring range, for example, when a human walks into the PIR detection range, it senses that the temperature in this range gets higher and this way the motion can be detected. PIR sensors can be adjusted to sense objects with higher or lower amount of emitted light, so the sensor picks up motion just by humans and not by animals.
PIR sensor is the most common type of motion sensor used in outdoor lights. PIR detectors are cheap to manufacture and they work pretty well in indoor and outdoor areas as they can be adjusted to pick up motion only by humans. If manufacturer has not indicated what type of sensor a lighting fixture uses, the chances are the light is equipped with a PIR motion detector. Flood lights with an infrared motion sensor are often described as “PIR lights”, “infrared lights”, “IR lights”, and as mentioned above, can also be described as a regular motion light.
More information about motion detectors
Bulb
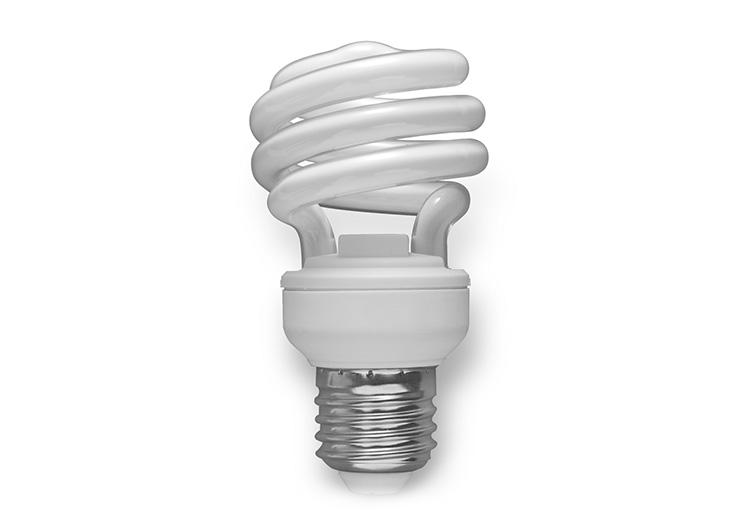
CFL bulb – Compact fluorescent light bulb is one of the most common type of light bulbs used in regular home lighting. You can mostly find CFL bulbs in ceiling lights, table lamps and similar lighting fixtures around the house.
CFL bulbs are also used in flood lighting, however, a lot less than LED or halogen bulbs because of their fragility, sensitivity to temperature changes, inability to instantly turn on to full brightness and reduction of lifetime when turned on and off regularly, properties that make them inappropriate for outdoor lighting. CFL bulbs also contain a toxic element – mercury which is dangerous for humans and the environment.
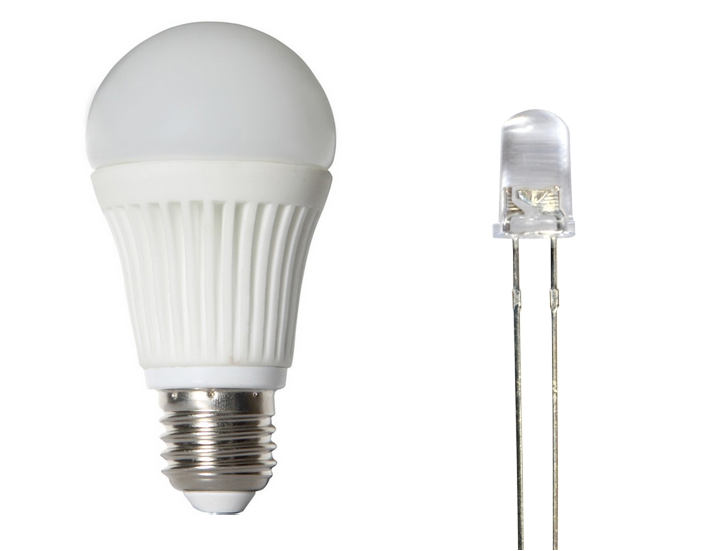
LED diode – LED diode or light-emitting diode is one of the newest type of light “bulbs” that uses significantly different technologies to create light, such as semiconductors and p-n junction diodes. LED diodes are becoming more popular not only in lamps used indoors, but also in outdoor lights, solar lights and are used in many other industries such as automotive industry.
LED diodes offer multiple advantages for indoor and outdoor lights. LED diodes have significantly longer lifespan than any other type of bulb, reaching 50000 hours on average. LEDs are also much more efficient and consume less energy than halogen or CFL bulbs, and this is one of the main reasons why LED diodes replace CFL bulbs in indoor lights and halogen bulbs in outdoor lights. Efficiency of LED is significant advantage for solar and portable lights. Besides these advantages, LED diodes are very small in their size and more durable than other bulbs, so that makes them the best bulb type for outdoor flood lights. LEDs, same as halogen bulbs turn on instantly and do not contain any toxic substances and can be dimmed. Currently the only disadvantage of LED diodes is that they cost significantly more than other type of bulbs, but the cost of LEDs is decreasing each year and savings on electricity by using LED diodes make up the high price of bulbs in few years of use.
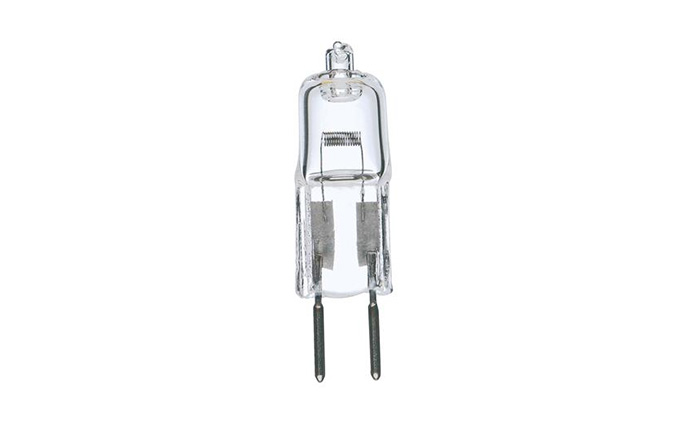
Halogen bulb – Halogen light bulbs are considered to be an upgraded version of old incandescent bulbs as the working principle of these lights is pretty similar to incandescent bulbs. Halogen bulbs are mainly used in lights that need to produce high level of brightness and need to illuminate large areas, such as flood lights. Halogen bulbs were the most popular bulb type used in flood lighting and other types of high tensity lighting, but now they are being replaced by more efficient LED diodes.
Halogen bulbs offer such advantages as high brightness, very good color rendering index, instantly turns on to full brightness, relatively compact size when compared to CFL bulbs and they also cost a lot less than their competitors – LED diodes. However, halogen lights also have some considerable drawbacks such as much lower efficiency as well as shorter lifespan than LED lights and halogen bulbs can get very hot when operating. Because of these factors, LED didoes are considered a better option for usage in outdoor flood lights and solar lights.
Incandescent bulb – Incandescent bulb is the “classical” light bulb that has been used for over 100 years and just recently is being replaced by other bulbs for indoor usage. Incandescent uses electricity to heat the filament which when heated to high temperature emits light. Incandescent bulbs are not used in flood lighting or solar lights.
Color rendering index – Color rendering index or CRI measures the ability of a light source such as a bulb to precisely render and show all colors of an object it illuminates when compared to perfect or natural light source which are incandescent light or daylight.
Color rendering index gets rated from 1-100 and also can be negative for some light sources. The highest CRI number is 100 for incandescent light. CFL lights usually have CRI of 70-80, LED lights over 85 and halogen lights 100 or close to 100 CRI.
Electric ballast – Electrical ballast is used to limit current into an electric circuit.
Ballasts are made in different complexities, for example in LED diodes you will find primitive ballasts such as resistors that limits current flowing trough a LED diode, however, in CFL bulbs a lot more complex ballasts need to be used, called inductive ballasts.
More information about LED, CFL and Halogen bulbs
Solar panel
Solar panel – Solar panels are devices used to collect energy from the sun and generate electricity using a photovoltaic effect.
Solar panel consists of multiple solar cells. Solar panels are used on buildings to provide electricity for a house, large quantity of solar panels are used on the ground in very sunny areas to generate high amount of electricity, and solar panels are also used to power smaller devices such as solar lights. The most popular types of solar panels currently used on houses and also on devices such as solar lights are monocrystalline, polycrystalline and amorphous solar panels.
Monocrystalline solar panel – Monocrystalline solar panels are the most efficient types of solar panels with cell efficiency of 15-21%, but at the same time are the most expensive. Monocrysalline cells are made from a pure silicon material with very small amount of other elements which is why the costs of monorcystalline panels are higher than of other panels.
Monocrystalline solar panels are mostly used on buildings and because of their efficiency are also widely used in higher end solar flood lights.
Polycrystalline solar panel – Polycrystalline panels are the second most common type of solar panels with efficiency from 13-16% which is lower than monocrystalline and higher than amourphous solar panel efficiency.
These solar panels have lower manufacturing costs because silicon material is used efficiently in the manufacturing of solar cells and the price for these panels is also significantly lower than monocrystalline price. Polycrystalline solar panels are also used on houses, larger industrial buildings and in solar panel farms on the ground. Polycrystalline solar panels are used in the same type of high end solar lights as monocrystalline panels because there isn’t a significant difference in the price and performance between both panels types at such a small size used to power solar lights.
Amorphous (thin-film) solar panel – Amorphous or thin-film solar panels are newer type of solar panels that are made from various materials with different manufacturing costs and efficiencies, such as Cadmium telluride (CdTe), Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), amorphous silicon (a-Si), Organic photovoltaic cells. These panels have efficiency of 10% and below based on the material used in the panel.
Thin-film solar panels are simpler and cheaper to manufacture and they can be made flexible, which allows to use them in large variety of devices. Amorphous solar panels are used in mid-range and low-range solar lights because they are a lot cheaper to make, which cuts down the total price of a lighting fixture. Thin-film panels are less efficient than monocrystalline or polycrystalline panels, so they are not the best solution for high power solar flood lights. However, they can still provide efficiency up to 10% which is enough to power a low brightness solar flood light and are perfect for powering other type of solar lights such as spot lights. Thin-film solar panel technology is still in a development process, so we might see more efficient thin-film solar panels in the future.
More information about solar panels
Battery
Rechargeable battery – A type of electrical battery that can be charged, discharged and recharged for multiple times.
Rechargeable batteries are also called secondary batteries while non-rechargeable batteries are called primary batteries.
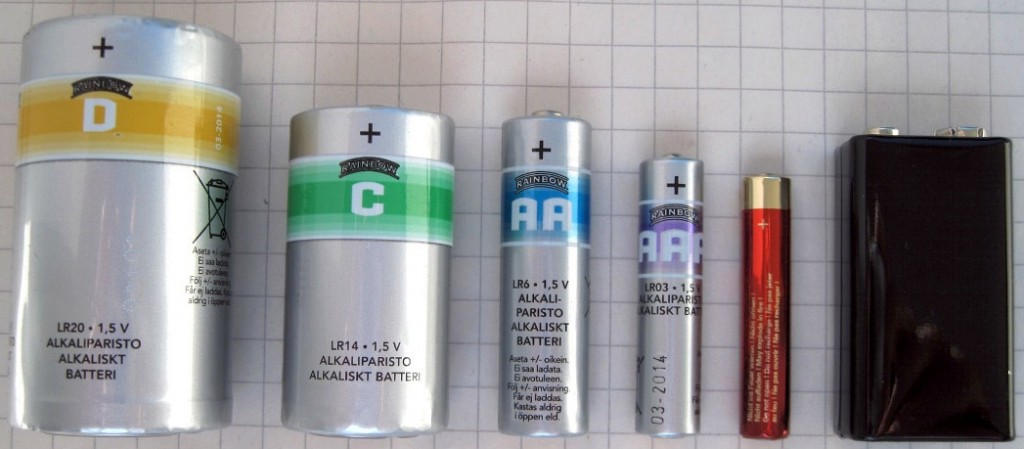
AA, AAA, C, D – Standard cylindrical battery sizes. Rechargeable battery types that are made in these standard cylindric battery sizes are Ni-Cd, Ni-MH and some Li-ion batteries.
Battery cycle life – Battery cycle life is used to describe how many time a secondary (rechargeable) battery can be charged and discharged until it starts to loose capacity.
The term cycle life is used to compare lifespans of different secondary batteries.
Ni-Cd battery – Ni-Cd is a rechargeable battery type used in small, portable electronic devices, power tools that require large amount of power released in short time and also in lower end solar and portable flood lights. Ni-Cd battery is also called nickel-cadmium battery, as it uses Nickel oxide-hydroxide as positive electrodes and Metallic cadmium as negative electrodes.

Ni-Cd were the most popular type of batteries until mid 1990s when majority of them were replaced with more efficient and environmentally friendlier Ni-MH batteries. Why Ni-Cd are not friendly for the environment? Because Ni-Cd battery contains a heavy metal cadmium which is toxic for humans and the environment and is difficult to dispose, this is why EU Battery Directive greatly restricted usage of Ni-Cd batteries in many appliances.
Ni-Cd batteries are available at same sizes as non-rechargeable alkaline batteries – from AAA to D, they have cell voltage of 1.2V and can maintain steady voltage while discharging. Ni-Cd batteries have cycle life of approx. 1000 cycles and their self-discharge rate is about 10%.
Ni-Cd batteries are mostly used in cheaper, less powerful solar flood lights and spot lights competing with Ni-MH batteries that have some significant advantages over Ni-Cd batteries. The advantages of Ni-Cd batteries in portable and solar lighting are their low price (Ni-Cd batteries are cheaper than Ni-MH and li-ion batteries), good cycle life and good low temperature tolerance, meaning that they can be used in outdoor flood lights in cold climate areas. However, their disadvantages of low capacity (approx. 2 times of Ni-MH and 3 times of li-ion), memory effect (if battery gets discharged to same level for multiple times it starts to loose some of its capacity) and toxic cadmium used in the battery, makes it the least preferred type secondary battery for lighting.
Ni-MH battery – Ni-MH, also called nickel-metal hydride battery, is a type of rechargeable battery used in small, portable consumer electronics and also in wide range of portable and solar lighting. Ni-MH batteries use hydrogen absorbing alloy as negative electrode instead of metallic cadmium used in Ni-Cd batteries, which makes them a lot more environmentally friendly. As Ni-MH batteries replaced Ni-Cd batteries in majority of consumer electronics, their size and form factor is very similar to that of Ni-Cd batteries, meaning that Ni-MH are also available in sizes from AAA to D, but mostly are used in battery packs.

The battery became commercially available in 1989 and till 2010 was the most popular type of battery used in portable consumer electronics, when it was being replaced by lithium-ion batteries in many industries. Ni-MH batteries are still very popular due to their high energy density (much higher than Ni-Cd and lead acid batteries), they can provide at least two times longer work time with one charge than similar Ni-Cd batteries but less than lithium-ion batteries. Cell voltage of Ni-MH battery is 1.2V and average cycle life about 800 cycles. These batteries can be rapid charged in about 1 hour. The biggest drawback of Ni-MH batteries is their high self-discharge rate, a typical Ni-MH battery will loose about 4-20% of its charge on first days and about 1% of its charge on the following days, which is almost 3 times higher than the self-discharge rate of a Ni-Cd battery and even more higher than the rate of li-ion and lead acid batteries.
Ni-MH batteries are used in sport lights and all range of solar flood lights, starting from cheaper, low end lights to expensive, high end flood lights, but you will mostly find them competing with Ni-Cd batteries in low end lights and lithium-ion batteries in midrange solar flood lights that are mostly used in household areas as decoration lighting, garden lights, patio lighting and security lights. On average, 3-5 AA battery packs with 2000mAh capacity of Ni-MH batteries are used in these lights.
The main advantages of Ni-MH batteries in portable lights are high capacity so they will provide longer work time with one charge which is useful in solar flood lights, they don’t develop any memory effects as Ni-Cd batteries and they are cheaper than li-ion batteries which also makes lighting fixtures with Ni-MH generally cheaper than similar fixtures with li-ion batteries. The main drawbacks are lower cycle life than Ni-Cd and lithium-ion batteries, high self-discharge rate and problems with over-charging and over-discharging, so a lighting fixture needs to have a special mechanism that can deal with this problem.
LSD-Ni-MH battery – LSD-Ni-MH or low self-discharge Ni-MH batteries were invented to solve the problem of high self-discharge rate of regular Ni-MH batteries. LSD-Ni-MH batteries have much lower self discharge rate, but to reach this they need to sacrifice some of their capacity and also bring up the price a bit when compared to regular Ni-MH batteries.
Most LSD-Ni-MH batteries can retain approximately 85% of their capacity at first year and up to 70% after 2 years of storage.
Li-ion/Lithium-ion battery – Lithium-ion or li-ion is currently the most popular type of rechargeable battery used in variety of industries and devices such as portable consumer electronics and automotive industry.
First lithium batteries were introduced in 1970s but these were non-rechargeable batteries that used the metallic lithium as anode material which is reactive and caused some serious safety issues, so scientists searched for ways to produce safer batteries using lithium. In the beginning of 1990s Sony introduced the first commercially available rechargeable lithium-ion battery. Unlike lead acid and other type of batteries that have reached their maximum potential, scientists are still working on ways to improve capacity, life time, power and safety of existing lithium-ion batteries and are developing new types of lithium-ion batteries each year. Lithium-ion batteries have certain advantages over other types of rechargeable batteries such as high energy density, which makes them the best suited battery type in portable electronics such as laptops, smartphones, tablets and also portable and solar lighting.
The most common li-ion battery types currently are Li-cobalt, Li-manganese, Li-phosphate and lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide or NMC battery. Each of these lithium-ion battery types have their own pros and cons and each is used in different industries. For example, li-cobalt batteries have higher capacity so they are used in portable consumer electronics such as laptops and smartphones, li-manganese batteries have higher power suitable for different power tools, li-phosphate batteries have long cycle life, wide operation temperature range and are safer, making them suitable for electric automobiles as well as portable and solar lighting, and NMC batteries provide the best overall performance making them the preferred battery type in electric vehicles.
A lithium-ion battery consists of pure lithium metal oxide as cathode (lithium cobalt oxide in li-cobalt batteries, lithium manganese oxide in li-manganese batteries, lithium iron phosphate in li-phosphate batteries and lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide in NMC batteries), porous carbon as anode, lithium salts with organic solvent as electrolyte. When li-ion batteries are charging, ions travel from positive electrode to negative and in opposite direction when batteries are discharging. Nominal cell voltage of li-cobalt battery is 3.6V, of li-manganese battery 3.8V, of li-phosphate battery 3.2/3.3V, of NMC battery 3.6/3.7V. Lithium-ion batteries are available in lots of different shapes and sizes form small coin shaped batteries, to AAA and AA batteries and large batteries used in electric cars. Self-discharge rate of li-ion batteries differ for each type of battery, but on average is 2-8% per month, the average lifespan is from 500-2000 cycles, li-cobalt batteries having the shortest lifespan and li-phosphate batteries (used in lighting fixtures) having one of the longest lifespans. The biggest advantage of li-ion batteries is the high specific energy meaning that they can store more energy per mass than Ni-MH, Ni-Cd and three times more energy than lead acid batteries, which the main reason why they are used in such a wide range of appliances. However, this comes with significant drawback, li-ion batteries have high manufacturing costs and high sale prices which is why batteries such as lead acid are still more popular as car batteries than li-ions.
In lighting, li-ion, similar to Ni-MH batteries are found in all range of lighting, starting from smaller solar spot lights to high powered portable flood lights, but are mostly used in mid-range and high-end lighting. Thanks to their high capacity, lithium-ion batteries are great for smaller portable and solar lights. The capacity of batteries used in these lights are usually from 2Ah up to 30Ah and more. The most common type of lithium-ion battery used in portable and solar flood lights and spot lights is the lithium phosphate or LiFePO4 battery which offers such advantages as great cycle life with up to 2000 charge, discharge cycles, large specific energy of 120Wh/kg, safety and ability to produce high currents for high power lighting systems.
The main advantages of using lithium-ion batteries for portable and solar lights are their high specific energy, so batteries can be made in much smaller size and weight while keeping the same capacity as other types of rechargeable batteries which is useful for smaller sized spot and flood lights, relatively low self-discharge rate, safety of li-phosphate battery, good cycle life up to 2000 cycles and they can also run maintenance free. The main drawbacks of these batteries for portable lights are higher manufacturing costs which results in higher price for lightning fixtures and low temperature intolerance, although li-phosphate batteries have improved low temperature tolerance and can work in temperatures below -20°C (- 4°F) which is very useful for outdoor flood lights.
Li-Phosphate (LiFePO4) battery – Li-Phosphate or LiFePO4 in short is a rechargeable lithium-ion battery used in variety of electronic products from portable consumer electronics to electric vehicles and it is the most common type of li-ion battery used in portable and solar lighting.
This battery type was first introduced in 1996 and now has developed to be one of the most widely used li-ion batteries. The characteristics of li-phosphate batteries when compared to other type of lithium-ion based batteries are safety, improved lifespan, ability to produce high currents, but they also have one of the lowest capacities of li-ion batteries.
Lead Acid battery – Lead acid battery is the oldest type of rechargeable battery that, in opposite to other battery types such as Ni-Cd, is still widely used today, mostly in automotive industry as starter battery.

The first lead acid battery was invented in 1859. As mentioned, the primary usage of lead acid batteries are in transportation industry as starter batteries, they are also used as backup power supplies and many high power flood lights and work lights are powered by lead acid batteries. There are two types of lead acid batteries – starting and deep cycle. Starting batteries can provide short and powerful burst of energy that is used, for example, to power automotive engines. In opposite, deep cycle batteries are designed for long term usage and can handle significantly more discharge cycles.
The main competitor to lead acid batteries are much newer and advanced lithium-ion batteries which are slowly taking market from lead acid batteries, but because of the cheap manufacturing process and the matured technology of lead acid batteries, they will not be fully replaced by lithium-ion batteries in the closest time, at least not in the automotive industry.
A lead acid battery consists of lead dioxide paste as positive plate, sponge lead as negative plate, sulfuric acid as electrolyte and the battery casing is usually made from plastic. These batteries are made from multiple cells and voltage of a single cell is 2.1 volts, so a 12V lead acid battery consists of 6 single cells. There are 3 more common types of lead acid battery – wet cell, which is the oldest type and mostly used as car starter batteries, Gel cell where electrolyte is in a gel consistency instead of liquid and AGM or absorbent glass mat batteries where glass microfiber mat separator is used between battery plates. The last two are also called VRLA or valve regulated lead acid batteries, they can handle very deep discharge cycles and can be used in any orientation thanks to a full sealing. Both valve regulated lead acid battery types are used in portable and solar flood lights.
The cycle life of lead acid batteries can vary from 500-3000 cycles based on the type of the battery, the self discharge rate is from 5-20% for wet cell batteries, but AGM lead acid batteries have a very low self discharge rate of approx. 2-3% a month, which is the lower rate between all rechargeable batteries. The biggest advantage of lead acid batteries is their low manufacturing costs, they have one of the lowest cost per watt hour of all rechargeable batteries which is the number one reason why they are still being used in so many industries. However, they also have some major drawbacks such as large size and weight which prohibits their usage in small, portable electronics and these batteries also have very low specific energy.
When talking about portable and solar lighting, lead acid batteries are mostly used in high power flood lights, but can also be found in some mid range lights. In opposite to other types of rechargeable batteries that are also used in solar spot lights, most of the time lead acid batteries are used to power flood lights or outdoor lighting systems. Lead acid batteries used in flood lights come in wide range of capacities from 4Ah up to 50Ah and even larger. Although lithium-ion batteries are slowly becoming the standard in many industries, including portable and solar lighting, lead acid batteries, because of their low manufacturing costs are still more common battery type for high powered flood lights.
The main advantages of lead acid battery usage in portable and solar flood lights are their cheap price, which also decreases the price of the lighting fixture, low self-discharge rate of Gel Cell and AGM batteries, low temperature tolerance (lead acid batteries can be used in low temperatures below -30°C, -22°F) and valve regulated batteries require very low maintenance. The main drawbacks of lead acid battery usage in portable and solar lighting are their low energy density, which means that lighting fixtures must be made in a larger size to provide the same capacity as other types of rechargeable batteries and the large size of these batteries also limits their usage so they are mostly used in high power lights. Lead acid batteries also have short cycle life of approx. 500 cycles, although newer Gell Cell and AGM batteries can reach cycle life of 2000 cycles.
AGM battery – AGM or absorbent glass mat battery is a type of the lead acid battery that uses glass microfiber mat separator between the battery plates. AGM batteries are also called valve regulated lead acid batteries, they are considered to be maintenance free, can be used in any orientation and have longer lifespan than regular lead acid batteries.
AGM batteries, similar as Gel Cell batteries, are used in high powered flood lights.